The Best Path to Mastering Artificial Intelligence - A Complete Guide (Part 2)
Let’s continue our roadmap by exploring the essential steps to fully dive into the world of Artificial Intelligence!
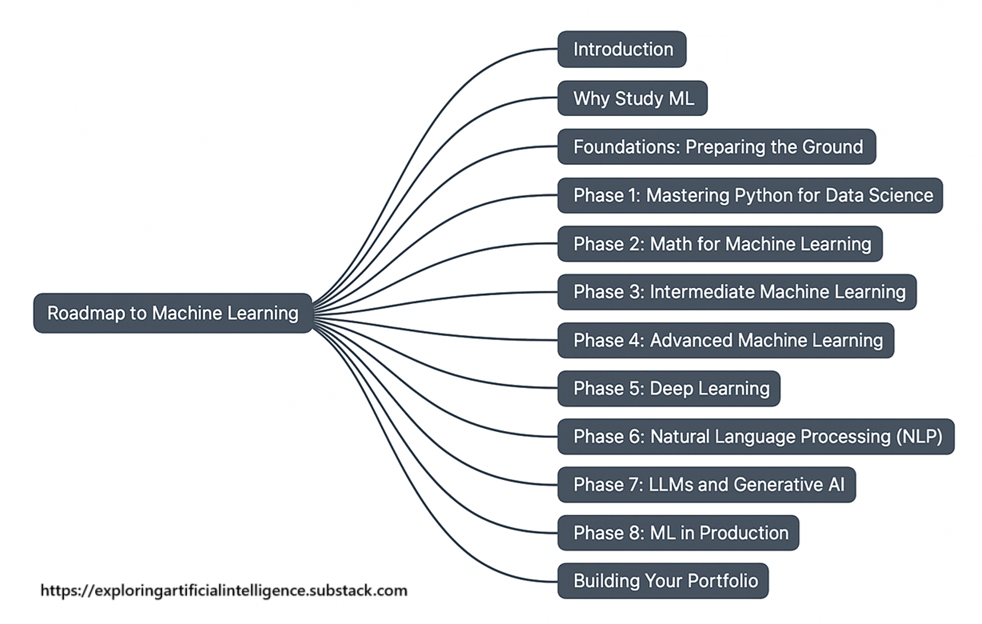
In the first part of our roadmap, we talked about the fundamental skills needed to start our journey in AI: Python programming, data analysis libraries, mathematics, and machine learning.
Now that we have a solid foundation, it’s time to take the next step. In this second part of the roadmap, we’ll delve into the universe of Deep Learning, NLP, Generative AI, and LLMs.
Phase 5: Deep Learning
Deep Learning has enabled remarkable advancements in fields such as computer vision, natural language processing, and many others. In this phase, we will explore the fundamentals of deep neural networks and their applications.
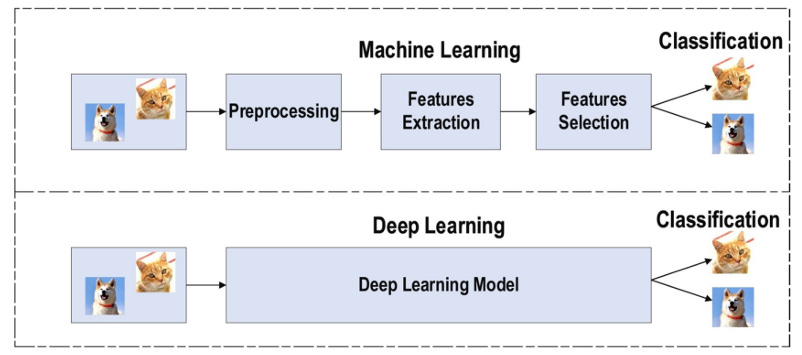
Deep Learning, also known as deep neural networks, is a subfield of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn complex data representations. Inspired by the functioning of the human brain, it allows algorithms to automatically extract relevant patterns and features from large volumes of data, without human intervention to manually define these rules.
Fundamental Concepts
Let’s start by understanding the basic building blocks of deep neural networks:
Deep Learning Specialization – A series of Coursera courses by Andrew Ng.
Deep Learning Book – A free online book by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville.
Deep Learning: Understanding Deep Neural Networks – An overview of deep learning.
Familiarize yourself with concepts such as artificial neurons, activation functions, backpropagation, optimizers, and regularization.
Popular Frameworks
Modern deep learning frameworks significantly simplify the development of complex models:
TensorFlow/Keras
TensorFlow 2 Quickstart – A quick introduction to TensorFlow 2.
Keras - Beginner's Guide – Introduction to Keras, TensorFlow's high-level API.
PyTorch
PyTorch Tutorials – Official tutorials for beginners.
PyTorch - Zero to GANs – A free online course.
Multilayer Perceptron Neural Networks (MLP)
MLPs are the most basic type of deep neural network, composed of a sequence of fully connected (dense) layers. Each neuron in a layer is connected to every neuron in the previous and next layer, allowing the network to learn complex patterns from tabular data, vectors, or numerical representations.
They are effective for classification and regression tasks when the data has no obvious spatial or sequential structure, such as in numeric datasets, user attributes, or sensor readings. Due to their simplicity and flexibility, MLPs are widely used as a starting point in deep learning and as the foundation for more complex architectures.
Multilayer Perceptrons in Machine Learning – A guide with basic concepts and functionality.
Tutorial Multilayer Perceptron – MLP tutorial with a practical example.
Multi-Layer Perceptron Explained – Practical guide for beginners.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs are a type of neural network designed specifically to process grid-like data, such as images. They use convolutional layers to automatically extract relevant features such as edges, textures, and shapes while preserving spatial relationships between pixels.
These networks excel in computer vision tasks such as object recognition, image classification, pattern detection, and segmentation. They are widely used in applications such as medical image diagnostics, autonomous vehicles, and intelligent surveillance systems.
An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) – Introduction to CNNs.
PyTorch CNN Tutorial – Create and train convolutional neural networks in Python.
CNN Implementation with TensorFlow/Keras – Practical tutorial.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs are designed to work with sequential data such as text, audio, or time series, as they have connections that allow for memory of previous information.
LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory) are a variant of RNNs with memory mechanisms that facilitate learning long-term dependencies in sequences. LSTMs are widely used in tasks such as machine translation, text generation, and speech recognition.
Sequence Processing with RNNs – Practical guide with TensorFlow.
Understanding LSTMs – Clear and visual explanation of LSTMs.
In addition to CNNs and RNNs, there are other deep learning architectures like Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCN), Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN), and Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). Although they are not covered in this roadmap, they are worth exploring in more advanced stages as your journey evolves.
Practical Deep Learning Projects
Apply your knowledge in projects such as:
Image Classification: Build a model that identifies different objects in images.
Time Series Forecasting: Use LSTMs to predict future values in time series.
Phase 6: Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP, or Natural Language Processing, is a field of AI focused on the interaction between computers and human language. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable machines to understand, interpret, generate, and respond to natural language.
As one of the most exciting and fast-evolving areas of AI -especially with the advent of Transformers and LLMs - in this phase we’ll explore the core concepts and modern techniques.
NLP Fundamentals
Let’s begin with the basic concepts of text processing:
Natural Language Processing Course – Coursera NLP specialization by Deeplearning.ai.
NLP with spaCy – Free text processing course using the spaCy library.
Kaggle Guide to NLP – Various resources on NLP.
Getting Started with Natural Language Processing – Free material from Microsoft.
Some key NLP concepts include: tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, part-of-speech tagging, named entity recognition, and sentiment analysis.
Word Embeddings
Word Embeddings are dense vector representations of words that capture their meanings based on the context in which they appear. Unlike traditional representations (such as one-hot), embeddings position words with similar meanings close to each other in the vector space.
Techniques like Word2Vec, GloVe, and FastText are popular examples, widely used in NLP tasks.
Word embeddings marked a major breakthrough in NLP by enabling machines to represent words with meaning, allowing semantic relationships such as "king - man + woman = queen". This approach overcame the limitations of sparse representations and paved the way for more sophisticated models.
Word2Vec Explained – Detailed explanation of Word2Vec.
The Illustrated Word2vec – Excellent guide to understanding Word2Vec.
GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation – Another popular technique for embeddings.
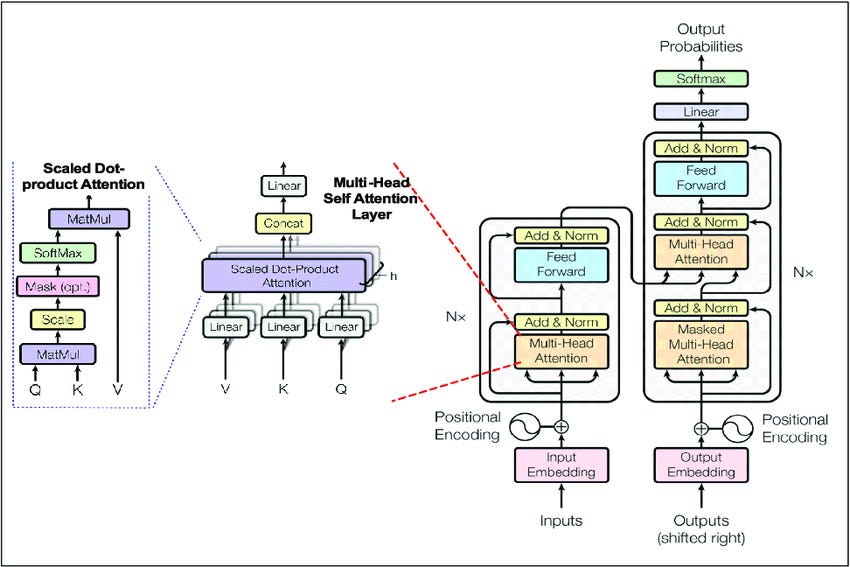
Transformer Architecture
The Transformer architecture revolutionized the field of NLP by eliminating the use of recurrence and convolutions (common in RNNs and CNNs) and by generating embeddings that consider the meaning of words in context, relying on attention mechanisms.
Introduced in the paper “Attention is All You Need” (2017), this architecture allows for processing entire sequences in parallel, significantly increasing efficiency and scalability. Its core component, attention, enables the model to focus on different parts of the input simultaneously, capturing long-range relationships between words.
This architecture serves as the foundation for powerful models like BERT, GPT, T5, and others, which dominate NLP tasks and even other areas such as computer vision and bioinformatics.
Attention is All You Need – Original paper that introduced the Transformer architecture.
The Illustrated Transformer – Excellent visual explanation of Transformers.
Generative AI exists because of the Transformer – Guide showing how the Transformer architecture and attention mechanism work.
How Transformer LLMs Work – Course covering the Transformer architecture and LLMs.
Hugging Face Course – Free course on Transformers and NLP.
Pretrained Models and Fine-Tuning
Pretrained models are artificial intelligence models that have gone through an initial learning stage on large volumes of data, acquiring general knowledge about language, images, or other domains. This pretraining allows the model to learn useful patterns and representations that can be reused in various applications.
Having a pretrained model, it can serve as a base for fine-tuning with task-specific data. This fine-tuning reduces training time, computational cost, and improves performance, especially in scenarios with few labeled data. This reuse accelerates the development of solutions in areas like NLP, computer vision, and bioinformatics.
The Illustrated BERT, ELMo, and co. – Guide on the main models based on the Transformer architecture.
A Visual Guide to Using BERT for the First Time – Understanding how BERT works.
Fine-tuning pretrained models – How to adapt models for specific tasks.
Practical NLP Applications
Try projects such as:
Text classification: Categorize texts by topic, sentiment, or intent.
Named entity recognition: Train a model to extract entities such as person, local, and organization.
Phase 7: LLMs and Generative AI
We’ve reached the current frontier of AI: Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI. These technologies are redefining what is possible with AI and opening new possibilities across virtually every field.
Large language models are models trained on a massive corpus (text collection) of data, capable of understanding and generating natural language fluently and coherently. Based on the Transformer architecture (already presented), LLMs such as GPT, LLaMA, and Gemini power Generative AI applications, enabling the creation of text, answering questions, translating languages, generating code, composing music, or even creating images, videos, and synthetic voices.
Foundations of LLMs
Understand how large language models work:
Generative AI with Large Language Models – Coursera course in partnership with AWS, covering generative AI fundamentals.
How Large Language Models Work – Complete and well-explained guide on LLMs.
Popular Models
Familiarize yourself with the main available models:
GPT (OpenAI) – Documentation for OpenAI’s models.
BERT and variants (Google) – Official repository of BERT and its variants (also available on HuggingFace).
Gemini (Google) – Google’s most advanced LLM.
LLaMA (Meta) – Open-source models from Meta (also available on HuggingFace).
Claude (Anthropic) – LLMs from Anthropic.
Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is an important skill for working with LLMs. It involves designing clear, specific, and well-structured instructions to guide the model’s output precisely and effectively.
Since LLMs are highly sensitive to how questions or commands are formulated, small variations in the prompt (input text) can result in completely different responses.
Mastering this technique allows you to explore the potential of models in tasks such as text generation, information extraction, summarization, translation, classification, and more - becoming an increasingly valued skill in generative AI projects.
Prompt Engineering Guide – Comprehensive guide on prompt engineering.
OpenAI Cookbook – Practical examples of effective prompts.
Google’s Guide to Effective Prompts with Gemini – Practical guide with best practices for effective prompts.
Projects with LLMs and Generative AI
Try projects such as:
Specialized virtual assistant: Create an assistant for a specific domain (e.g., medicine, law, education).
Creative writing tool: Develop an application that helps with creative writing by providing suggestions from an LLM.
End of Part 2
In this second part of the roadmap, we’ve covered the concepts of deep learning, natural language processing, and generative AI.
In the final part, we’ll continue with the concepts of:
Ethical considerations
MLOps and Deployment
Tips for building your portfolio
Thank you for reading❣️
See you in Part 3!!